There are three alternatives:
- Beacon Wireless
- Telus Smarthub (or similar cellular-data solution)
- Starlink
Beacon Wireless
Beacon Wireless offers a long-distance WiFi solution using a dish antenna pointed at towers on Pender or Saturna islands. It needs line-of-sight to one of those. The dish is usually mounted on a building or a tall tree, by a technician who installs the unit.A cable runs from the dish to an interface which both powers the transceiver on the dish and acts as a NAT router. Beacon do not supply the password. You need an ethernet switch and optionally WiFi access point in your home. You get IP addresses on a private network assigned to your devices.

Wireless dish
Power supply and ethernet routerPerformance
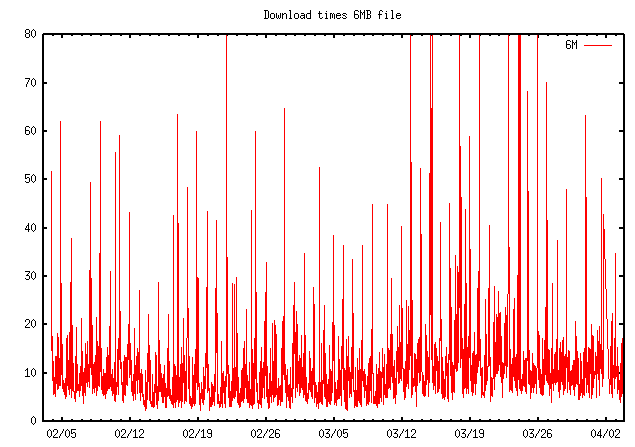
Time in seconds to download a 6MB file, January 2022Telus Smarthub
Telus offers a cellular data solution, consisting of a combination cell transceiver, ethernet switch and WiFi NAT router. You get IP addresses on a private network assigned to your devices. The router contains a small backup battery to power the device for a while during a power outage. It has to be placed somewhere that gets a good cell signal; mine seemed best in my garage, which I have wired for ethernet.Telus offers a newer Smarthub device that is capable of 5G speeds, but there are no 5G towers on the island
 Performance
Performance
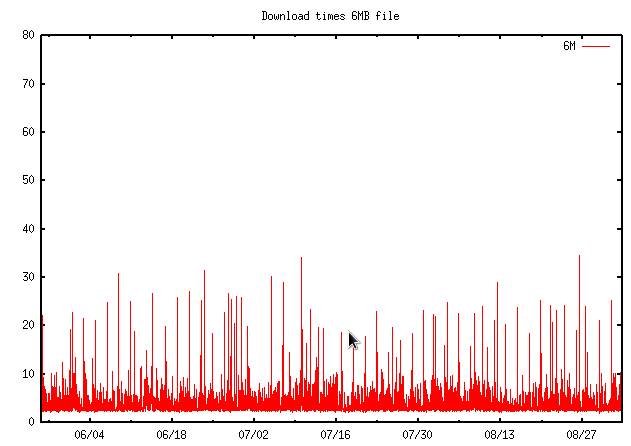
Time in seconds to download a 6MB file, 2022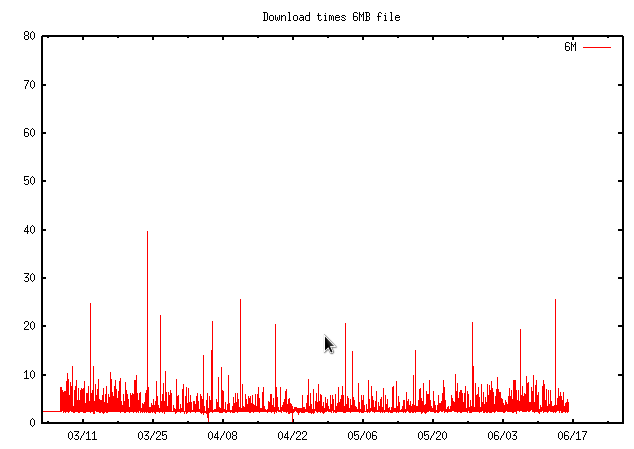
Time in seconds to download a 6MB file, 2023Flood ping 11 June 2023
2000 packets transmitted, 1987 received, 0.65% packet loss, time 24673ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 81.739/135.088/297.055/38.965 ms, pipe 27, ipg/ewma 12.342/132.711 ms
Starlink
Starlink offers a satellite-based solution using a constellation of satellites in close Earth orbit. The data connection is handed off between many satellites as they move across the sky, so that the active one is always physically quite close giving good latency.The equipment consists of a motorized antenna array and a combination power supply and WiFi NAT router connected by a cable. Both units are weatherproof. You get IPv4 addresses on a private network assigned to your devices. The router also supports IPv6. The standard device is WiFi only. Starlink also sell an Ethernet inferface to connect to a local network.
Configuration and setup is via a cellphone app for Android or iOS. The antenna needs an unobstructed view of the sky directly above, and the app uses the phone camera, acceleratometers and compass to determine if a particular location is suitable. Generally, the higher the better if the home is surrounded by trees. Once the device is powered up and running, it will gather its own statistics over a 12-hour period and create an animation of the obstructions. The app can also create a map of a house showing the WiFi strength in different areas.

Satellite antenna
Power supply and WiFi router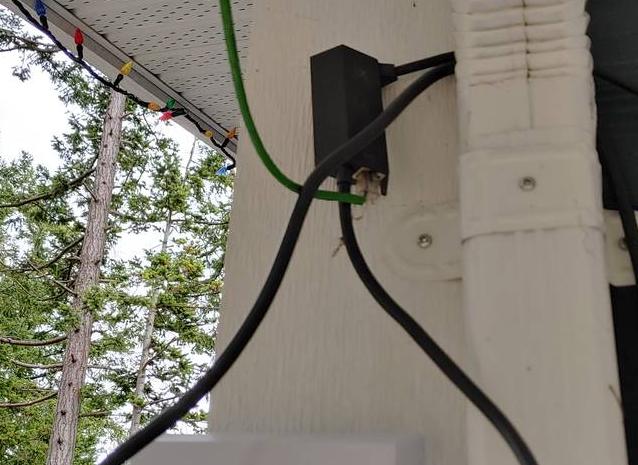
Ethernet interface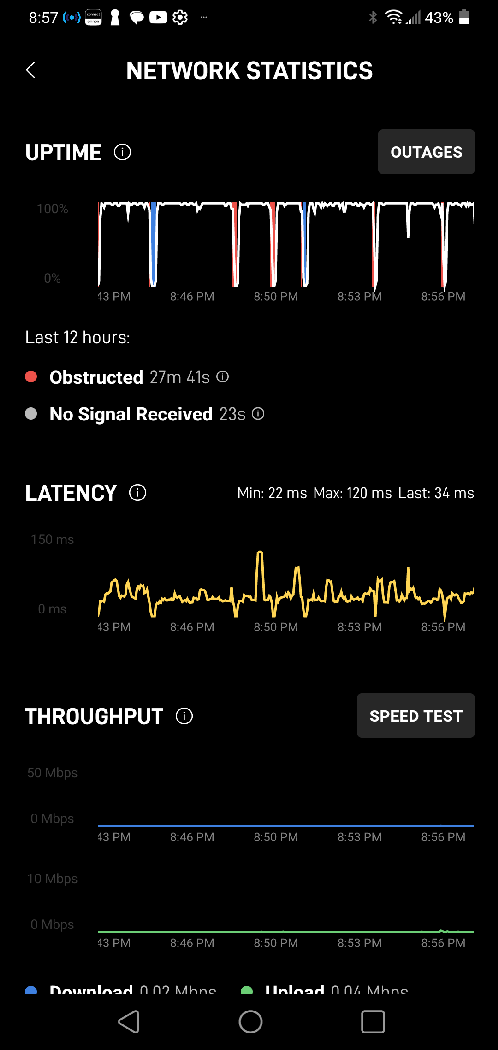
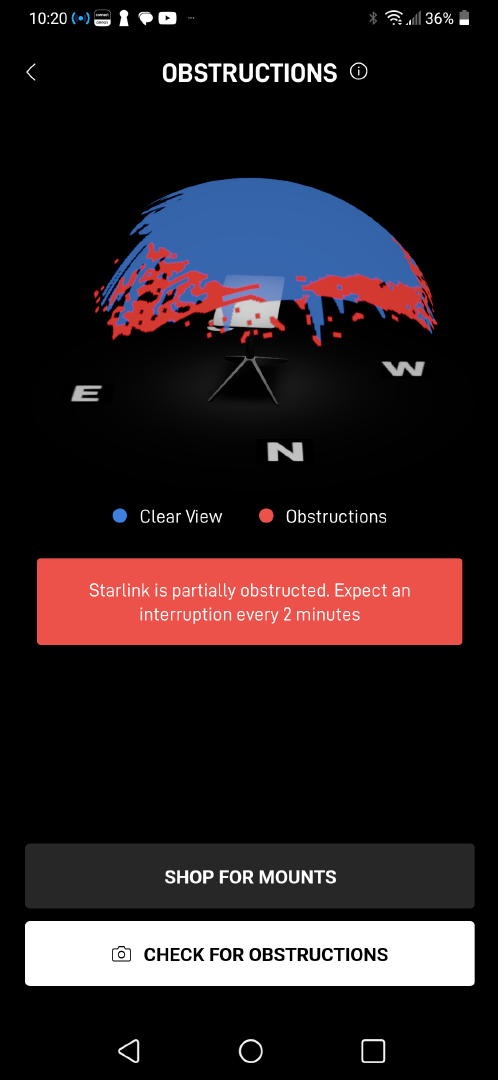
Smartphone app with the antenna on my deck, i.e. badly obstructed.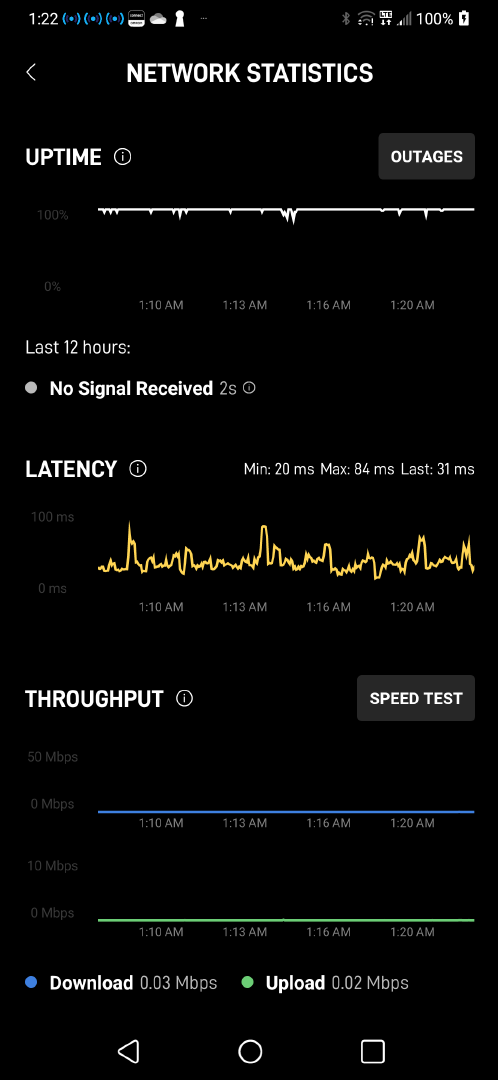
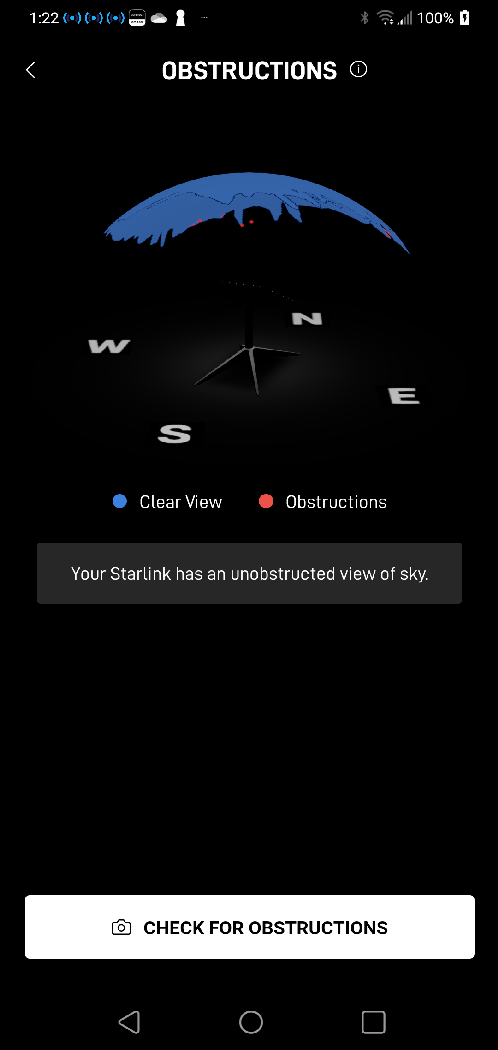
Smartphone app with the antenna on the roof peak, as in the photo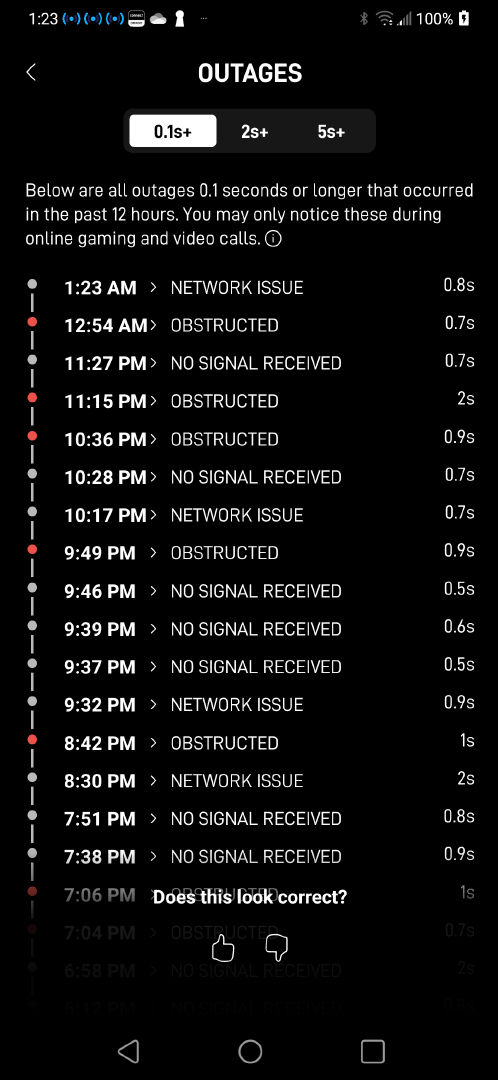
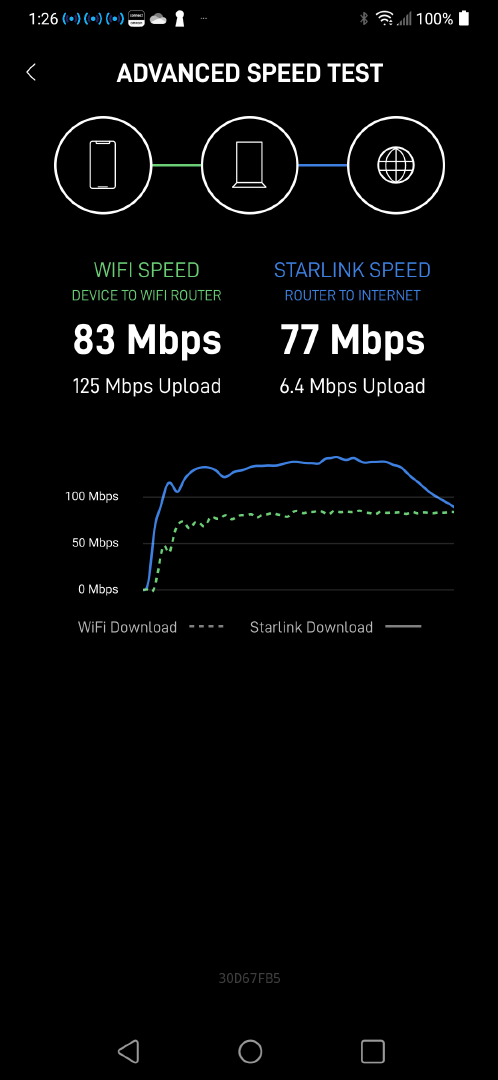
Outage list and Starlink's own speed testPerformance
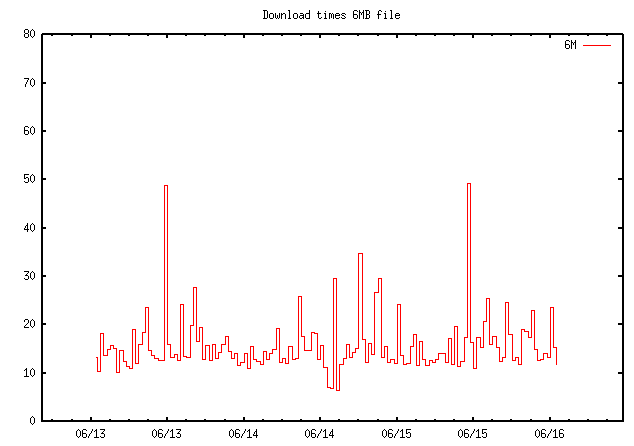
Time in seconds to download a 6MB file, June 2023Flood ping 11 June 2023
2000 packets transmitted, 1987 received, 0.65% packet loss, time 24673ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 81.739/135.088/297.055/38.965 ms, pipe 27, ipg/ewma 12.342/132.711 ms
Flood ping 19 June 2023, via ethernet cable, to this server2000 packets transmitted, 2000 received, 0% packet loss, time 28281ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 80.409/96.363/171.960/10.433 ms, pipe 13, ipg/ewma 14.147/92.474 ms
Flood ping 19 June 2023 to www.google.com on IPv61000 packets transmitted, 998 received, 0% packet loss, time 13707ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 21.440/35.146/98.086/10.050 ms, pipe 6, ipg/ewma 13.720/32.682 ms
Flood ping 19 June 2023 to www.google.com on IPv41000 packets transmitted, 1000 received, 0% packet loss, time 13449ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 42.400/54.606/92.230/9.409 ms, pipe 8, ipg/ewma 13.462/53.295 ms
Traceroute to www.google.com on IPv4
traceroute to www.google.com (142.250.217.68), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets 1 100.64.0.1 42.901 ms 53.477 ms 53.439 ms 2 172.16.250.20 53.436 ms 53.420 ms 53.397 ms 3 206.224.64.20 53.394 ms 206.224.64.46 53.372 ms 206.224.64.200 53.306 ms 4 206.224.64.135 53.215 ms 53.182 ms 206.224.64.39 53.167 ms 5 142.250.163.222 58.415 ms 142.250.170.144 53.189 ms 53.142 ms 6 * * * 7 142.251.55.200 36.647 ms 142.251.48.212 47.084 ms 142.251.55.200 56.984 ms 8 142.251.55.197 46.986 ms 142.250.217.68 46.955 ms 74.125.243.202 56.861 ms
Traceroute to www.google.com on IPv6traceroute to www.google.com (2607:f8b0:400a:80b::2004), 30 hops max, 80 byte packets 1 2605:59c8:200:df67::1 25.720 ms 25.637 ms 32.304 ms 2 2620:134:b0fe:250::20 32.292 ms 32.259 ms 32.227 ms 3 2620:134:b0ff::18c 32.230 ms 2620:134:b0ff::174 32.158 ms 32.187 ms 4 2620:134:b0ff::16f 31.991 ms 2620:134:b0ff::21b 31.931 ms 2620:134:b0ff::1e7 31.882 ms 5 2001:4860:1:1::f86 31.909 ms 31.922 ms 31.863 ms 6 2607:f8b0:832f::1 31.842 ms 2607:f8b0:8001::1 27.848 ms * 7 2001:4860:0:1::52b4 20.819 ms 2001:4860:0:1::255a 20.769 ms * 8 2001:4860:0:4::3 20.665 ms 2001:4860:0:4::2 31.206 ms 2001:4860:0:4::6 37.781 ms 9 2001:4860:0:1041::1 37.766 ms * 37.665 ms 10 2001:4860:0:1::5635 37.567 ms 37.563 ms 37.505 ms 11 2607:f8b0:400a:80b::2004 37.413 ms 37.366 ms 23.642 ms